Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects 1 out of 15 women during their child-bearing years. But, symptoms can occur early in their teenage years. In the long run, if left untreated, chances of getting heart disease and diabetes type II are very high.
The cause of PCOS is unknown. But, research says PCOS is most likely hereditary caused by changes of hormone levels. There is high androgen levels yet low progesterone levels which prevent ovulation and cause irregular menstrual cycle or amenorrhea (absent).Women with PCOS also have too much insulin in the system that the body has problems using them. This problem is called insulin resistance. Excess insulin can cause blood glucose level anomalies and androgen production anomalies.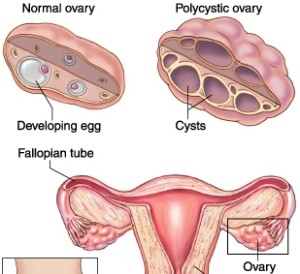
The egg does not mature and the fluid-filled follicle just grows in size but does not break open for ovulation to occur. The follicle stays in place and become subcapsular cyst. Multiple subcapsular cysts are present on the ovary, hence it is called polycystic ovary.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
• Acne.
• Oily skin
• Dandruff
• Weight gain and difficulty losing weight. Some have extra weight around the waist.
• Thinning hair on the scalp.
• Hirsutism- too muc hair growth on the body especially on the face.
• Skin tags- flaps of skin on the neck, armpit, breasts, or thighs.
• Pelvic pain
• Irregular menstrual periods/ amenorrhea. Some women have very heavy bleeding.
• Infertility (difficulty getting pregnant)
• Sleep apnea – while asleep, breathing stops for a short period of time.
• Depression
COMBINED TESTS TO RULE OUT PCOS:
1. Family History of Diabetes Mellitus or PCOS
2. Medical History of menstrual cycle patterns and weight changes
3. Physical Exam – Get blood pressure and check physical appearance like presence of excessive hair, acne, skin tags, and more.
4. Blood Tests to check androgen hormone levels and glucose levels in the blood.
5. Ultrasound – Either of the two can be done: transvaginal (through the vagina) or transrectal (through the rectum) to see images of the ovary with presence of multiple cysts.
6. Pelvic Exam to check enlargement of cyst.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome treatments:
- EXERCISE- Reduce weight or keep weight at a healthy level.
- DIET- Avoid too many sweets, white rice and other carbohydrates.
- MEDICATIONS- Doctors usually prescribe diabetic medications such as Metformin. This does not only control blood glucose level, but also improves body mass and lowers testosterone & cholesterol levels.
If you’re not planning on getting pregnant as of the moment, you can take birth control pills as this can improve menstrual cycle, clear acne, and reduce production of male hormones. - OVARIAN DRILLING- Surgery that increases the chance of ovulation and decreases male hormones. Laprascopic procedure is done by inserting a long instrument and then puncturing the ovary with a needle. This needle carries an electric current which shocks and destroys part of the ovary. However, this is a last resort for women wanting to get pregnant because ovarian drilling may leave a scar on the ovary.
For more information visit the following sources: http://women.webmd.com/tc/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos-topic-overview, http://womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/polycystic-ovary-syndrome.cfm

Hello admin do you need unlimited articles for your page ?
What if you could copy post from other sources, make it pass copyscape test and publish on your
page – i know the right tool for you, just
search in google:
Loimqua’s article tool